Problems and Countermeasures in the Construction and Management of Modular Clean Operating Rooms
Author: Han Guangying
Affiliation: Infection Management Department, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University
Related Concepts
Clean Room
A room where the concentration of airborne suspended particles is controlled. The construction and use of the room should minimize the introduction, generation, and retention of particles indoors as much as possible. Other related parameters in the room, such as temperature, humidity, and pressure, are controlled according to requirements.
—ISO14644 Cleanrooms and Associated Controlled Environments
Modular Clean Operating Room
An operating room that uses air purification technology to reduce the microbial particles and total particulates in the surgical environment air to permissible levels.
—GB50333-2013 Architectural Technical Specification for Hospital Clean Operating Departments
Modular OR Air Conditioning System
A system that primarily uses filtration for sterilization and dust removal to control the concentration of suspended dust and microorganisms in the controlled area to the required levels.

—GB50333-2013 Architectural Technical Specification for Hospital Clean Operating Departments
Clean Operating Room ≠ Laminar Flow Operating Room
Clean rooms are classified by airflow type: unidirectional flow (laminar flow) clean rooms, non-unidirectional flow clean rooms.
Unidirectional flow (laminar flow): Air flows at a uniform sectional speed along parallel streamlines.
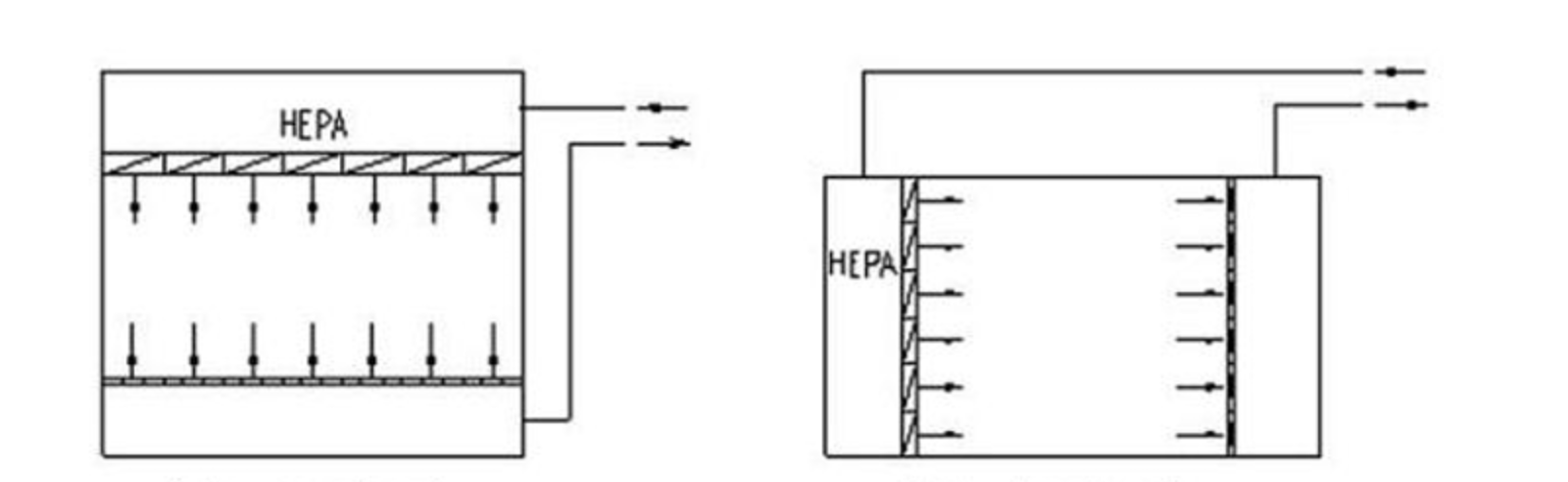
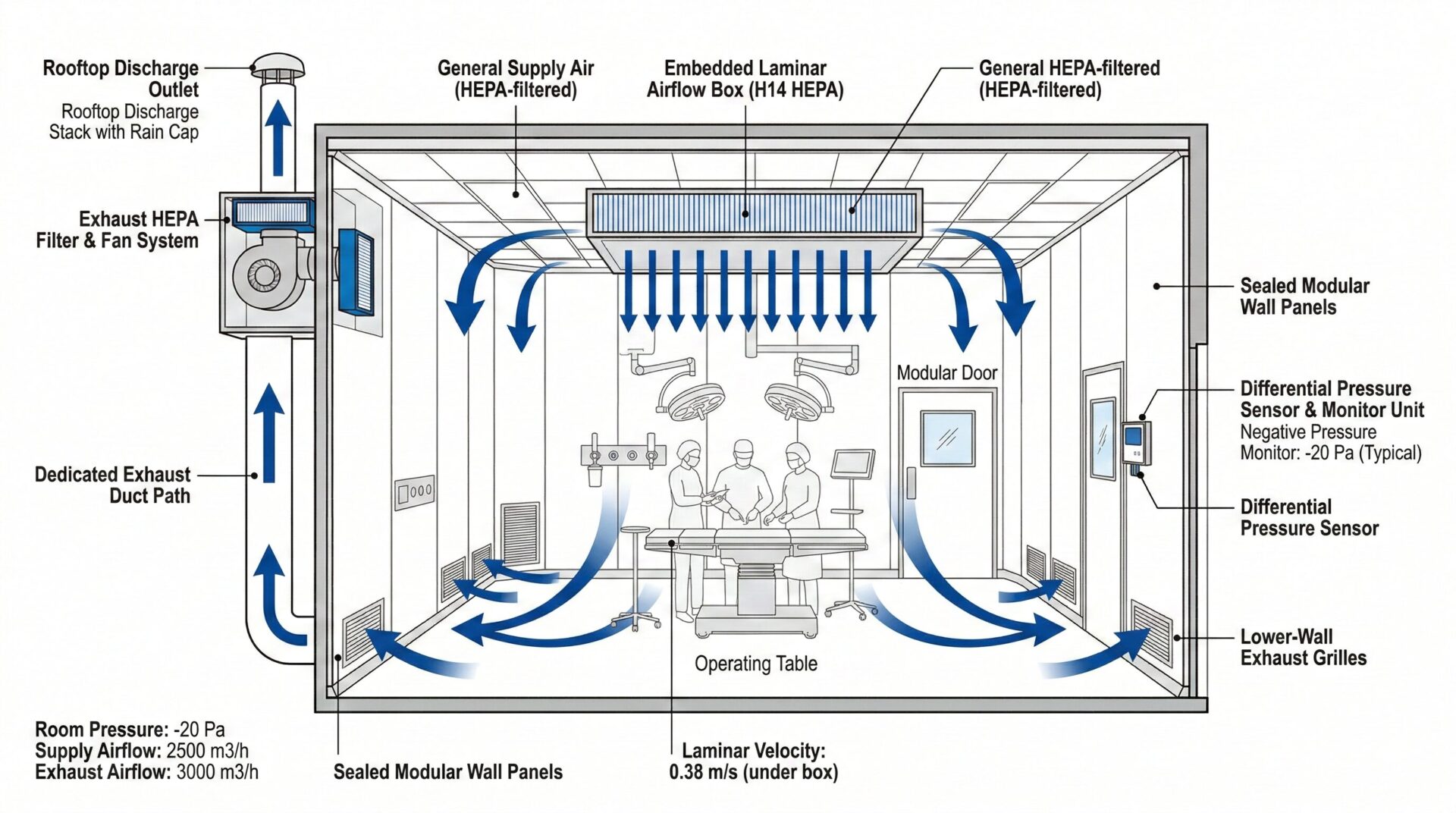
The purification principle of non-unidirectional airflow is the dilution principle. General forms include high-efficiency filter air supply outlets at the top for air supply; return air forms include lower return air, side lower return air, and top return air, etc.

Remarks: Return air terminal position in different position to realize non-unidirectional airflow
Problems in the Construction and Management of Clean Operating Departments (Rooms)
- Blind Construction
- Substandard Quality
- Inadequate Maintenance
- Non-standard Monitoring
- Unscientific Management

In the survey, 80% of general hospitals have built clean operating rooms, with no significant differences in the proportion of clean operating rooms across different levels and different numbers of open beds.
1. Blind Construction
Do Hospitals Need to Build Clean Operating Rooms?
How do standards and guidelines require it?
- Hospital operating rooms are divided into general operating departments and clean operating departments.
—GB51039-2014 Comprehensive Hospital Architectural Design Specification
- To standardize the design, construction, and acceptance of hospital clean operating departments, improve the medical environment control ability of hospital clean operating departments.
—GB50333-2013 Architectural Technical Specification for Hospital Clean Operating Departments
- Eye surgeries can be performed in ordinary operating rooms.
Guidelines for Eye Surgery Management, Infection Control, Disinfection and Sterilization in China
- Laminar ventilation systems should not be used to reduce the risk of SSI in patients undergoing total hip replacement surgery.
WHO Global Guidelines for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection (2016)
Clean operating rooms are just an option for operating room construction.
Advantages
- Full-process control dynamic assurance system ensures the supply of clean air.
- Pressure difference control eliminates the leakage of polluted air from outside.
Disadvantages
- Expensive to build, high operation and maintenance costs.
- Clean technology can only clean the air entering the clean room and cannot control pollution sources brought into the operating room by other means.
- Poor management can bring risks.
Rational Approach to Hygiene Operating Room Construction
- It is not recommended to widely promote the construction of clean operating departments. Hospitals should determine based on their scale, combining the types of surgeries conducted and needs, as well as the hospital’s financial and management capabilities!
- The cleanliness level of clean operating rooms should fully consider operational economy and clinical effectiveness. The higher the cleanliness level, the higher the construction cost, operating expenses, and energy consumption.
- Trend: A small number of clean operating rooms coexisting with more general operating rooms.
2. Substandard Quality
The clean operating department construction market is quite chaotic, and quality is worrying.
- Design: Process, parameters, layout, flow.
- Designed by non-medical architectural design institutes.
- The purification part is handled by construction units through “secondary deepening design”.
- Not based on the actual situation of each hospital. Countermeasures:
- Clean technology experts should participate from the start of design (floor height, load-bearing).
- Avoid designing while constructing.
- First process design, then architectural design.
- Pre-design review system.
- Construction: Construction units vary in quality; many without experience and qualifications in clean operating room construction are undertaking projects.
- Professional construction teams.
- Construct according to standards.
- Construct according to design drawings.
- Acceptance: Completion acceptance and third-party testing.
- Total 132 inspection items, including 27 key items and 105 general items.
- Any incomplete or missing items are called defect items. GB50591 Clean Room Construction and Acceptance Specification
Third-Party Comprehensive Performance Evaluation Testing
Testing 10 indicators for comprehensive performance: air bacterial concentration, cleanliness level, sectional wind speed, ventilation times, fresh air volume, static pressure difference, noise, illumination, temperature, relative humidity, etc.
Must be tested and archived by professional engineering quality inspection institutions or third-party institutions with laboratory accreditation qualifications before use.